What is inflammation?
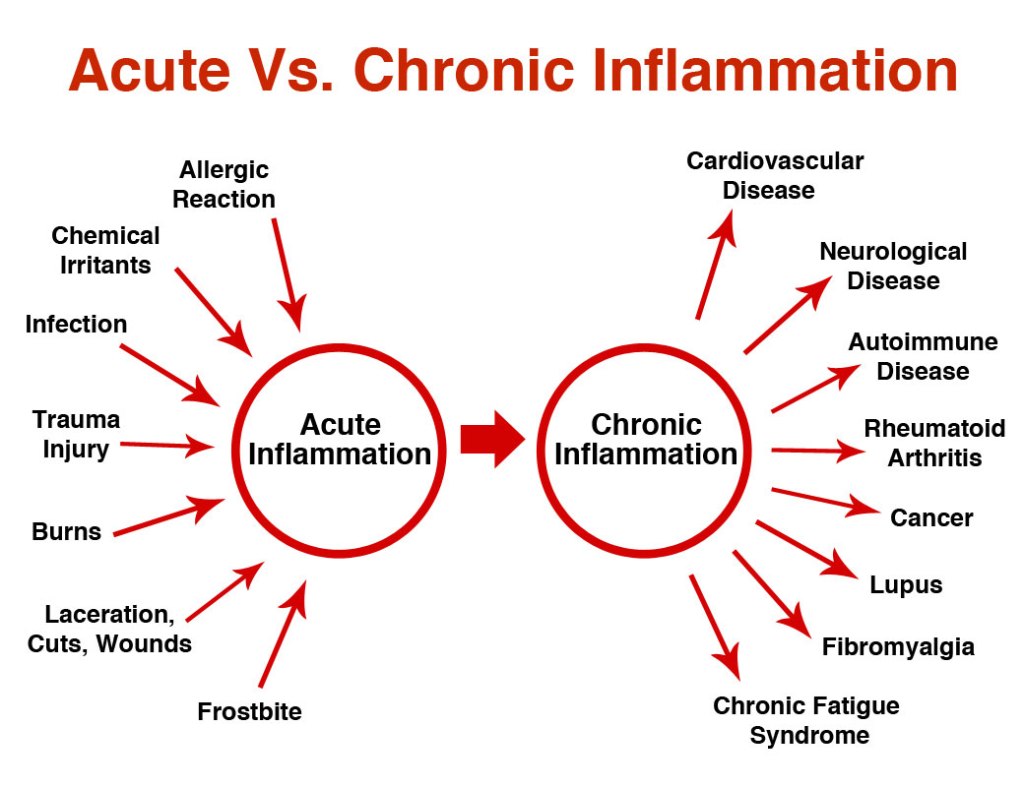
Inflammation refers to your body’s process of fighting against things that harm it, such as infections, injuries, and toxins, in an attempt to heal itself. When something damage your cells, your body releases chemicals that trigger a response from your immune system. This response includes the release of antibodies and proteins, as well as increased blood flow to the damaged area. The whole process usually lasts for a few hours or days in the case of acute inflammation. Chronic inflammation happens when this response lingers and leaving your body in a constant state of alert. Over time, chronic inflammation may have a negative impact on your tissues and organs. Chronic inflammation could also play a role in a range of conditions, from cancer to asthma.

The symptoms of chronic inflammation.
Acute inflammation often causes noticeable symptoms such as pain, redness or swelling. But chronic inflammation symptoms are usually subtler. This makes them easy to overlook. The common symptoms of chronic inflammation are rashes, fatigue, mouth sores, fever, abdominal pain and chest pain. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and last for several months or even years.

What causes chronic inflammation?
Several things can cause chronic inflammation which include;
- untreated causes of acute inflammation, such as an infection or injury.
- an auto immune disorder which involves your immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissue.
- long term exposure to irritants such as industrial chemicals or polluted air.
Bearing in mind that these do not cause chronic inflammation in everyone. Some cases of chronic inflammation do not have a clear underlying cause. Experts also believe that a range of factors may also contribute to chronic inflammation, such as obesity, smoking, alcohol and chronic stress.
How does chronic inflammation impact the body?
When you have chronic inflammation, your body’s inflammatory response can eventually start damaging healthy cells, tissues and organs. Over time, this can lead to DNA damage, tissue death, and internal scarring. All of these are linked to the development of several diseases which include obesity, asthma, type two diabetes, arthritis, heart disease, cancer and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
How is chronic inflammation treated?
Inflammation is a natural part of the healing process. The moment it becomes chronic, it’s important to get it under control to reduce your risk of long term damage. Here are some of the options that have been explored for managing inflammation.
Non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
NSAIDs such as aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen effectively reduce inflammation and pain. But long term use is linked to an increased risk of several conditions, including peptic ulser and kidney disease.
Steroids.
Corticosteroids are a type of steroid hormone. They decrease inflammation and suppress the immune system which is helpful when it starts attacking healthy tissue. The down side is long term use of corticosteroids can lead to vision problems, high blood pressure and osteoporosis. The doctor will weigh the benefits and risks with you before prescribing corticosteroids.
Supplements.
Certain supplements may help to reduce inflammation. Fish oil, lipoic acid and curcumin are all linked to decreases inflammation associated with diseases, including cancer and heart disease. Several spices may also help with chronic inflammation and inflammatory disease including ginger, garlic, and cayenne.

How does diet impact chronic inflammation?
What you eat can play both a positive and negative role in managing chronic inflammation. A variety of foods have anti inflammatory properties. These include foods that are high in antioxidants and polyphenols for example nuts, tomatoes, olive oil, fruits like blueberries and oranges, leafy greens like spinach and fatty fish like salmon. If you’re looking to rethink your eating habits, consider trying the Mediterranean diet. Study shows that those following this diet had lower markers of inflammation. This adds to the health benefits found in other studies on the Mediterranean diet.
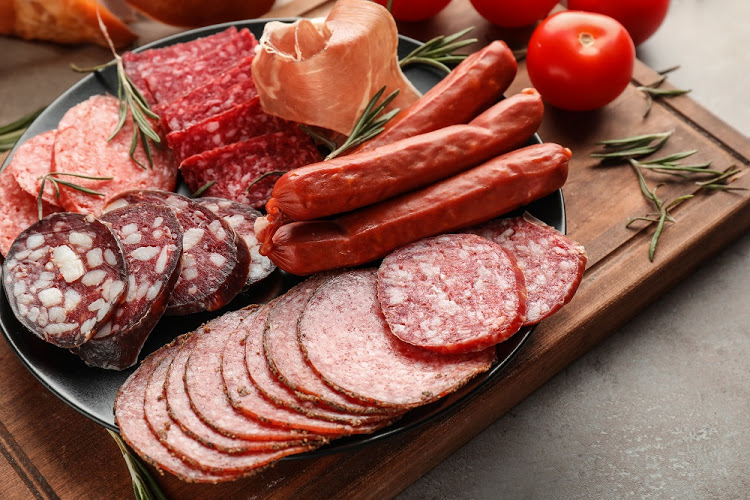

Having said all that, there are also foods to avoid though. Red meat, processed meat, fried foods and refined carbohydrates like pastries and white bread, can increase inflammation in some people. Try reducing intake of these foods. You do not have to completely eliminate them, but try to eat them only occasionally.
Basically, chronic inflammation increases your risk of several serious diseases. Inflammation can diagnose inflammation using blood tests. Medication, supplements, and eating an anti inflammation diet can help you reduce your risk of inflammation. Avoiding smoking and alcohol, and maintaining a healthy body weight can also help lower your risk, along with reducing your stress levels.